What is Perforated Metal and Its Uses in Construction and Design
Perforated metal has emerged as a versatile and innovative material in the realms of construction and design, offering a unique blend of aesthetics and functionality. According to industry expert Dr. Emily Turner, a leading architect specializing in sustainable materials, "Perforated metal not only enhances the visual appeal of a structure but also plays a crucial role in improving its environmental performance." This duality makes perforated metal an invaluable asset for architects and designers alike.
From facades and ceilings to railings and interior features, perforated metal finds its applications in various aspects of architectural projects. Its ability to allow light and air flow while maintaining structural integrity sets it apart from traditional materials. As urban spaces become more complex and the demand for sustainable design increases, the use of perforated metal is becoming more prevalent, inviting creativity and innovation in modern architecture. This article delves into the various uses of perforated metal in construction and design, exploring how it can transform spaces while adhering to contemporary sustainability practices.
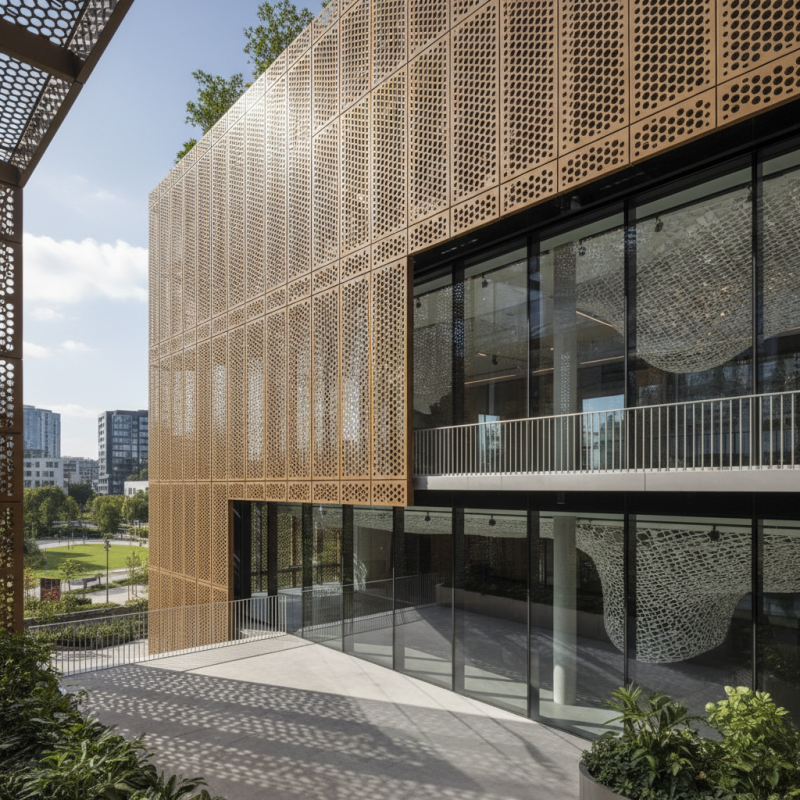

What is Perforated Metal? Definition and Composition Explained

Perforated metal is created by punching a series of holes into a sheet of metal, transforming it into a versatile material that blends functionality with aesthetic appeal. Typically made from materials like steel, aluminum, or copper, the composition of perforated metal can vary, providing different levels of strength and design flexibility. The pattern, size, and spacing of the holes can be customized, enabling architects and designers to achieve specific visual effects while enhancing airflow, light diffusion, and sound absorption in various applications.
When considering the use of perforated metal, it is essential to keep in mind its diverse functionalities. It is commonly employed in construction for facades, sunshades, and privacy screens, where it provides both structural integrity and design flair. In interior design, perforated metal panels contribute to contemporary aesthetics in partitions, ceiling tiles, and furniture, offering a unique blend of style and practicality.
Tips for using perforated metal include selecting the right hole size and pattern to meet the specific needs of your project—whether for decorative purposes or functional constraints like ventilation and filtration. Additionally, consider the type of finish and coating best suited for the environment in which the metal will be installed, as this can impact both durability and maintenance.
Key Manufacturing Processes of Perforated Metal in the Industry
Perforated metal, characterized by its unique pattern of holes, serves various functions in construction and design, where its manufacturing processes play a crucial role. The primary methods for creating perforated metal include mechanical punching, laser cutting, and water jet cutting. According to a report by the Grand View Research, the global perforated metal market was valued at USD 1.2 billion in 2021 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% from 2022 to 2030. This surge in demand emphasizes the importance of efficient and innovative manufacturing techniques in meeting industry requirements.
Mechanical punching remains the most widely utilized method in the production of perforated metal due to its efficiency and cost-effectiveness, accommodating both small and large runs. Laser cutting, while offering precision and versatility in complex designs, is increasingly favored for applications requiring tighter tolerances. Water jet cutting provides additional benefits through its ability to cut intricate patterns without thermal distortion. These manufacturing processes allow for customization in design, catering to architectural elements such as facades, ceilings, and partitions while contributing to sustainability by utilizing recyclable materials. A recent industry analysis by Research and Markets highlighted that sustainable building practices have driven an increased interest in perforated metals, accounting for a notable part of the overall growth trajectory in construction and design sectors.
Common Applications of Perforated Metal in Construction Projects
Perforated metal, a material characterized by its unique holes and patterns, is widely utilized in various construction projects due to its versatility and aesthetic appeal. One of the most common applications of perforated metal is in facades and cladding systems. Architects and designers often favor it for creating visually interesting exterior surfaces that allow light and air to pass through while maintaining privacy and protection from the elements. This feature not only enhances the aesthetic quality of a building but also contributes to energy efficiency by reducing heat gain.
In addition to facades, perforated metal finds application in interior design, particularly in architectural elements such as railings, ceiling panels, and room dividers. The ability to customize hole sizes and patterns enables designers to achieve specific visual effects, making perforated metal a popular choice for modern interior spaces. Moreover, it provides functional benefits like sound absorption and improved airflow, making it an ideal choice for high-traffic areas. Its lightweight properties and strength also make it suitable for various structural components, showcasing the practicality and adaptability of perforated metal in both construction and design.
Design Advantages of Using Perforated Metal in Architectural Design
Perforated metal is increasingly becoming a favored material in architectural design due to its unique blend of functionality and aesthetic appeal. One of the primary design advantages of perforated metal is its ability to create visually striking facades while providing practical benefits such as light diffusion and ventilation. According to a report by the International Journal of Architectural Research, the use of perforated materials in building designs can reduce energy consumption by as much as 20% by improving natural lighting and airflow within structures. This eco-friendly characteristic makes it highly attractive for sustainable building practices.
Moreover, perforated metal allows architects to experiment with various patterns and styles, enabling custom designs that resonate with the surrounding environment. Recent studies indicate that incorporating perforated metal in a building’s design can enhance its acoustic performance, a vital aspect in urban settings where noise pollution is a concern. By strategically using perforated panels, architects can manipulate sound waves, reducing reverberation and making interior spaces more comfortable. The National Association of Architectural Metal Manufacturers highlights that these acoustic properties contribute to improved occupant satisfaction and are increasingly being utilized in commercial and residential applications, showcasing the versatile role of perforated metal in contemporary architecture.
Industry Trends and Future Prospects for Perforated Metal Usage
The trend of using perforated metal in construction and design is continuously evolving, driven by a growing emphasis on sustainability and aesthetic versatility. Architects and designers are increasingly recognizing the benefits of perforated metals, including their ability to enhance ventilation, reduce weight, and offer unique visual properties. The incorporation of this material not only meets functional needs but also contributes to the overall aesthetic appeal of buildings and structures. As urban environments prioritize sustainability, the demand for perforated metal as a lightweight and recyclable building material is expected to increase.
Future prospects for perforated metal usage look promising, particularly with advancements in technology that enable more intricate patterns and designs. Innovations in cutting and finishing techniques allow for unique applications, ranging from facades and sunshades to interior partitions and decorative elements. Additionally, as environmental concerns shape the industry, manufacturers are likely to focus on developing eco-friendly production processes, further elevating the appeal of perforated metal in modern architecture. As cities continue to grow and transform, perforated metal will play a vital role in creating functional and visually striking spaces that align with contemporary design philosophies.
Perforated Metal Usage in Construction and Design by Industry
Related Posts
-

What is a Perforated Metal Sheet? A Comprehensive Guide to Its Uses and Benefits
-
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Stainless Steel Mesh Screen for Your Home Projects
-

Top 5 Benefits of Using Expanded Metal Sheets for Your Projects
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Stainless Steel Wire Mesh
-

What is Welded Wire and How to Choose the Right Type for Your Projects
-

Choosing the Right Trench Drain Grate for Your Home Landscape Needs
